IoT networks: SigFox vs LoRa
LPWANs (Low Power Broadband Networks) are a type of wireless communication networks designed for long-range communications, but they can only handle very low data rates.

These networks are perfectly suited to the IoT use case, where connected objects send small amounts of sensor-generated data and run on battery power.

SigFox is a French company that positions itself as an IoT network provider and aim to become the main global provider of IoT networks.
- In this network, the devices send their data through the SigFox network to a SigFox backend, and Sigfox handles the transfer of the messages by making an HTTP request to a preconfigured backend.
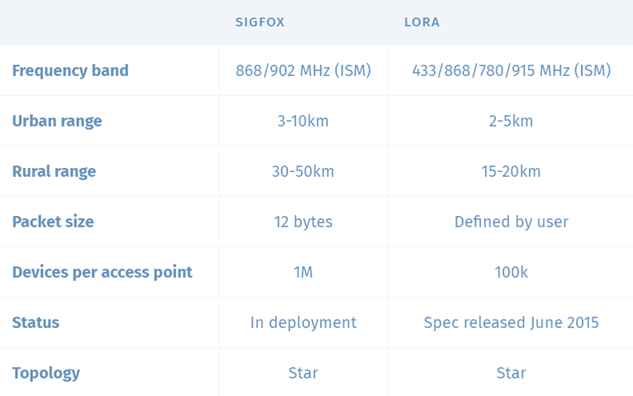
- SigFox is an Ultra-NarrowBand technology that works with sub-GHz frequencies in radio bands: 868MHz in Europe / ETSI and 902MHz in the United States / FCC.
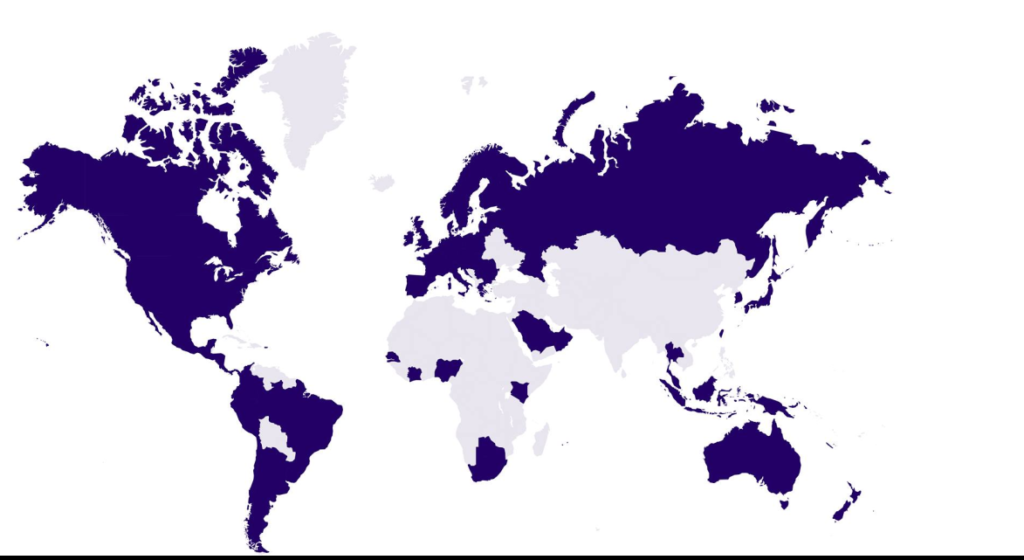
- As of April 2020, the network covers 50 countries (coverage), and the company deploys its antennas with the help of local telecom companies around the world, so the IoT provider does not have to worry about setting up the infrastructure.
- SigFox also has a number of restrictions on messages transferred over the network, where each device can send only 140 messages per day with a limit of 7 messages per hour (each message can be up to 12 bytes in length).
- The radio modules are also capable of receiving 4 incoming transmissions per day.
- SigFox fully manages the communication between the IoT device and the application backend, which makes the integration of the radio module a fairly easy process for developers. A single API is provided to interact with the radio module, no configuration required.
- To start integrating SigFox, it is necessary to purchase a compatible radio module and a renewable subscription plan for your device.

LoRa is a proprietary long-range wireless technology standard that operates in the radio frequency spectrum: 863 to 870 MHz in the EU / 902 to 928 MHz in the United States.
- It is a PHYsical layer (OSI Layer 1) protocol that provides a low-power, long-range communication medium for machine-to-machine (M2M) and IoT applications.
- LoRa technology was originally developed by Semtech, but is now managed by the “LoRa Alliance”. Any hardware manufacturer can build LoRa modules, but they have to obtain a compliance certification from the alliance.
- LoRaWAN is an open protocol built on top of LoRa.
- While LoRa offers simple point-to-point message delivery, the LoRaWAN protocol manages the communication of devices with the application backend and provides an end-to-end encryption and authentication scheme.
- Unlike SigFox, standard LoRa modules can work bidirectionally. Using the same radio module, a receiver can act as a transmitter.
- Therefore, LoRa is more suited to command and control scenarios.
- Unlike SigFox, the LoRa Alliance does not want to position itself as a network provider – its goal is to develop a standard and sell chips, so there is no monopoly on the LoRA network.
If you want to use LoRa for your product, you have 2 options:
- Deploy your own network: Anyone can buy chips and create their own network of devices, gateways, and backends. Besides, you will have to implement and maintain both the gateways and the devices, but you will have full control over your network and be able to adapt and modify it as your product grows and your needs change.
- Use a network operator’s network: Several operators are starting to offer LoRaWAN networks in certain areas. In the future, connectivity plans may be purchased from them, although coverage and service continuity must be ensured.
Comparing SigFox and LoRa
Although both networks are located in the same sector in IoT, they have very significant differences:
Aunque ambas redes se sitúan en el mismo sector en IoT tienen diferencias muy significativas:
- SigFox is defined as a global IoT operator while LoRa wants to position itself as a technology that can be integrated by operators to obtain a global IoT network.
- Unlike SigFox, LoRA modules can operate bidirectionally. This way, LoRa is more adapted to Command and Control scenarios.
- SigFox offers a very simple API to integrate communication with devices, while LoRa offers a more configurable API, which can complicate the integration of LoRa radio modules.
- SigFox messages are limited by design to 12 bytes. In LoRa the size of a message is defined by the user, although they must comply with regularizations.
- SigFox allows to identify and authenticate devices.