The National Security Scheme (ENS) and the Onesait Platform (part II)
Last week we told you what the National Security Scheme consisted of and its importance. As we mentioned, the Onesait Platform takes this scheme into account, with a large number of these measures resolved by the design of its architecture.
Having said that, let’s see how it fits:
- Accredited services. Services provided by a system with authorization granted by the responsible authority, to process a specific type of information, under precise conditions of the security dimensions, in accordance with its concept of operation.
- Active. A component or functionality of an information system that can be deliberately or accidentally attacked, with consequences for the organization. This includes: information, data, services, applications (software), equipment (hardware), communications, administrative resources, physical resources and human resources.
- Authenticity. Property or characteristic consisting of the fact that an entity is who it claims to be, or the fact that it guarantees the source from which the data comes.
- Availability. Property or feature of the assets assets consisting in that authorized entities or processes having access to those when required.
- Basic security principles. Fundamentals that should govern any action aimed at ensuring information and services.
- Category of a system. It is a level, within the Basic-Medium-High scale, with which a system is described in order to select the necessary security measures for it. The category of the system includes the holistic view of the set of assets as a harmonic whole, oriented to the provision of services.
- Confidentiality. Property or feature consisting in the fact that the information is neither made available nor disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities, or processes.
- Electronic signature. Set of data in electronic form, consigned together with others or associated with them, which can be used as a means of identification of the signatory.
- Electronic signature policy. Set of security, organizational, technical and legal standards to determine how electronic signatures are generated, verified and managed, including the characteristics required of signature certificates.
- Incident Management. Action plan to deal with incidents that occur. In addition to solving them, it must incorporate performance measures that allow knowing the quality of the protection system and detect trends before they become big problems.
- Information security management system (ISMS). Management system that, based on the study of risks, is established to create, implement, operate, supervise, review, maintain and improve information security. The management system includes the organizational structure, the policies, the planning activities, the responsibilities, the practices, the procedures, the processes and the resources.
- Information system. Organized set of resources so that information can be collected, stored, processed, maintained, used, shared, distributed, made available, presented or transmitted.
- Integrity. Property or feature that proves that the information asset has not been altered in an unauthorized manner.
- Minimum security requirements. Necessary requirements to ensure information and services.
- Network and information security is the ability of networks or information systems to resist, with a certain level of confidence, accidents or illicit or malicious actions that compromise the availability, authenticity, integrity and confidentiality of data, either stored or transmitted, and of the services that said networks and systems offer or make accessible.
- Process. Organized set of activities that are carried out to produce a product or service; it has a delimited beginning and end, it involves resources and produces a result.
- Risk. Estimation of the degree of exposure to a threat materializing on one or more assets causing damage or harm to the organization.
- Risk analysis. Systematic use of available information to identify hazards and estimate risks.
- Risk management. Coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with respect to risks.
- Security audit. Independent review and examination of system logs and activities to verify the adequacy of system controls, ensure compliance with the established security policy and operating procedures, detect security breaches, and recommend appropriate modifications to controls, policy and procedures as appropriate.
- Security incident. Unexpected or unwanted event with consequences that are detrimental to the security of the information system.
- Security measures. Set of provisions aimed at protecting against possible risks to the information system, in order to ensure its security objectives. These can be prevention, deterrence, protection, detection and reaction, or recovery measures.
- Security policy. Set of guidelines included in a written document, which govern the way in which an organization manages and protects the information and services that it considers critical.
- Security process. The method followed to achieve the organization’s security objectives. The process is designed to identify, measure, manage and keep under control the risks faced by the system in terms of security.
- Traceability. Property or characteristic consisting in that the actions of an entity can be attributed exclusively to said entity.
- Vulnerability. A weakness that can be exploited by a threat.
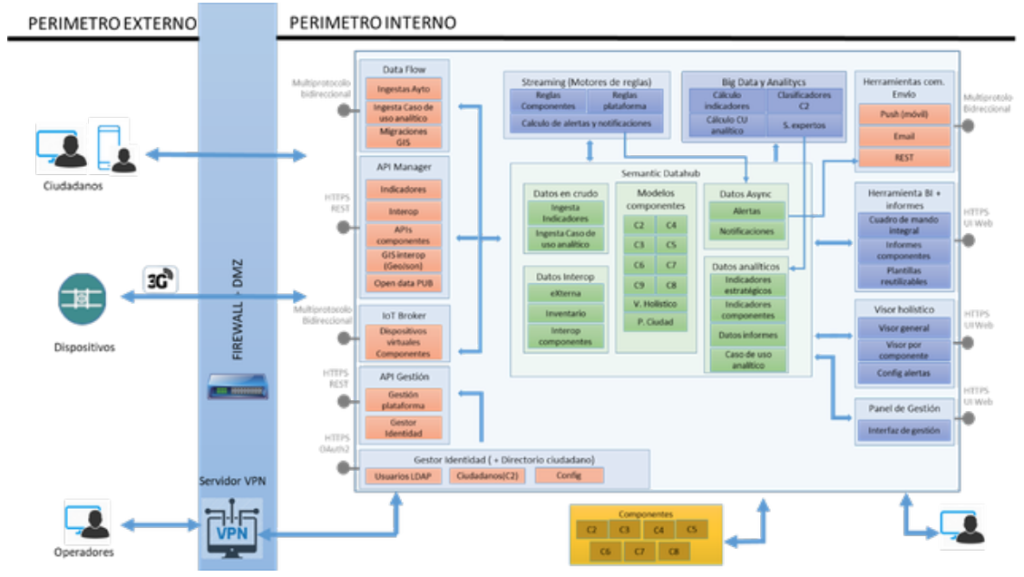
As we can see, the Onesait Platform adapts to the needs of the National Security Scheme, with the addition that we can adapt it project by project, according to their needs. Thus, for example, in the Project that we have in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, we have adapted without problems the security requirements that we have been requested:
So: yes, the Onesait Platform is a secure platform that meets standards and is adaptable to the needs of each client.





